If you’ve ever used any application or platform for long enough, you know one thing for certain: no software is perfect. Bugs and errors are, unfortunately, unavoidable parts of the user experience. While they may be only an inconvenience in regular apps, in CRMs the consequences of vulnerabilities are far more serious. These systems store customer records filled with private information, sales, and sometimes financial data. A flaw in this type of software can lead to a major data breach and reputational damage.
Open-source CRMs play by their own rules when it comes to bugs. The publicly available code allows communities to identify and fix problems quickly, but users have to stay vigilant and apply updates regularly, because delays leave systems exposed to vulnerabilities.
Why bugs happen in Open-Source CRMs
Bugs in open-source CRMs are a result of several factors:
Complexity of CRM systems
CRM systems offer many features and modules to handle every aspect of customer relationships: leads, deals, marketing emails, support requests, reports, etc. As all tools are interconnected, minor changes during the updates in one area can introduce unexpected behaviour or issues in another.
Constant development
The software is always changing. Open-source projects often follow a “release-early-and-often” philosophy and introduce new features as soon as the basic functionality works. Then, they expect that community testing will catch the real problems. Although this approach gets new capabilities to users faster, it also allows bugs and security issues to appear when people start using the software for routine tasks.
Variety of environments and configurations
Every user has a different setup. The same CRM might be installed on different operating systems, run in different web browsers, hosted on servers with different configurations, and have different third-party integrations. Each combination of configurations creates potential compatibility issues, and testing every variation is practically impossible for volunteer-driven projects.
Rating open-source CRMs by their vulnerabilities
When businesses select open-source CRMs, they compare features, the activeness of communities, documentation, and how easy it is to customize them. But in this process, it’s also vital to consider the software stability. How prone is the solution to bugs and how severe are they?
To help answer these questions, we analyzed the publicly reported vulnerabilities for five popular platforms: EspoCRM, Odoo, Vtiger, SuiteCRM, and Dolibarr.
How we assessed these systems
We used publicly available data from the National Vulnerability Database (NVD), which tracks official security issues called CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures), as of November 12, 2025. During the analysis, we considered the number of issues, severity, and average CVSS of the vulnerabilities.
This ranking is not the complete picture. We used publicly available data on issues that were discovered, reported, and assigned official CVE numbers. Many vulnerabilities probably exist and haven’t been found or have been fixed without public disclosure.
The popularity and age of the software also affect our data. Systems that have been on the market longer and have more users are examined more closely by security researchers and attackers alike. This often leads to more documented vulnerabilities not because the software is necessarily less secure, but because more eyes are looking for problems.
Finally, different development teams handle security disclosure in different ways. Some are very transparent about reporting every security fix, others patch issues without formal CVE submissions. That said, the public data we used might not reflect the true security picture for every platform equally.
| CRM System | Initial Release | Total CVEs | Avg. CVSS Score | Critical | High | Medium | Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EspoCRM | May, 2014 | 33 | 6.1 | 0 | 7 | 24 | 2 |
| Odoo | February, 2005 | 49 | 6.9 | 5 | 13 | 31 | 0 |
| Vtiger | December, 2004 | 71 | 6.6 | 6 | 26 | 37 | 2 |
| SuiteCRM | October, 2013 | 85 | 7.8 | 19 | 37 | 28 | 1 |
| Dolibar CRM | September, 2003 | 125 | 7.2 | 29 | 32 | 64 | 0 |
Detailed analysis per CRM
EspoCRM
Issue Count: 33
EspoCRM shows the cleanest record among the reviewed CRMs. The issues are mainly medium and low-level bugs ranging from cross-site scripting (XSS) to LDAP injection.
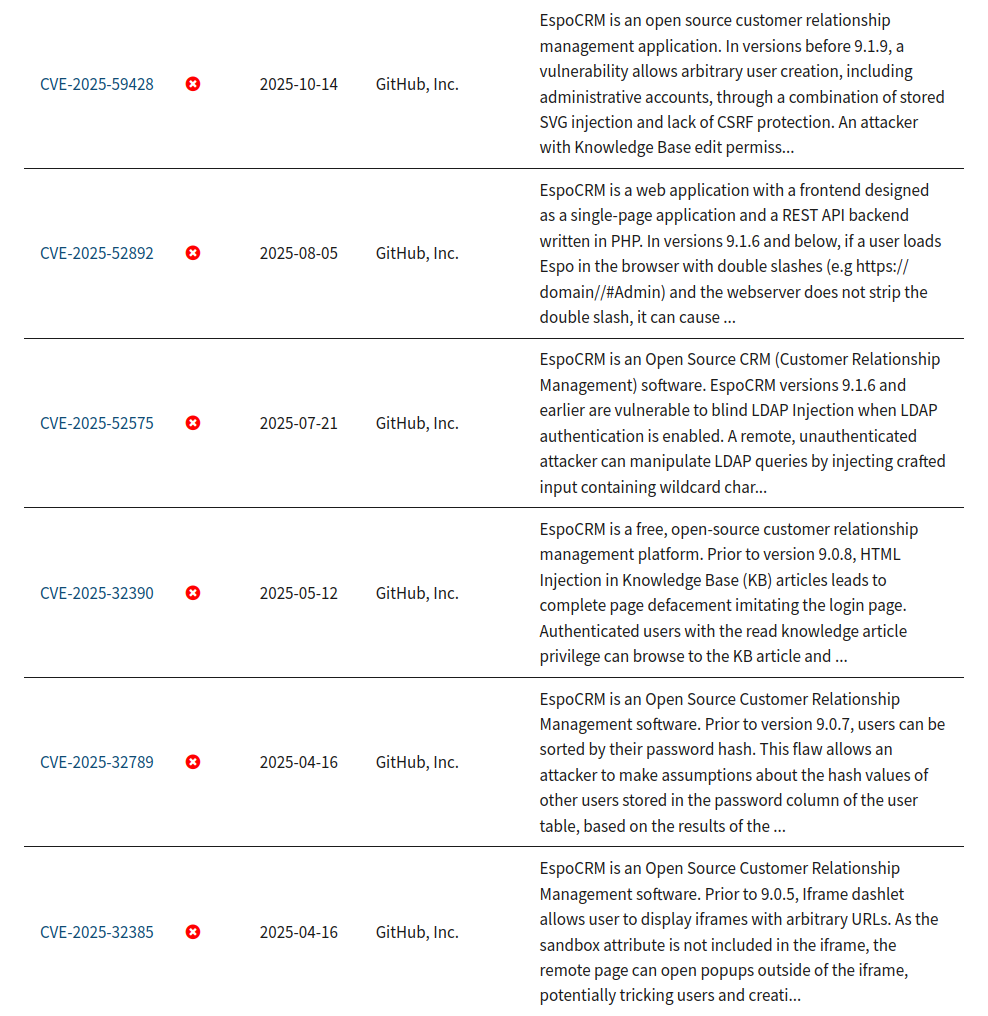
EspoCRM has had several injection-related vulnerabilities reported in recent versions, including a 2022 CSV injection that can lead to command execution, a later HTML injection that allows interface defacement, and a recently disclosed blind LDAP injection.

The discovery of vulnerabilities in EspoCRM has fluctuated over the years. The highest number of issues was reported in 2019 (12 CVEs). Recent years: 2022 (4 CVEs), 2023 (3 CVEs), 2024 (1 CVE), and 2025 (6 CVEs) show fewer problems. This pattern suggests that security research into the system may have been inconsistent but has identified 7 significant issues in certain periods.
Odoo
Issue Count: 49
Odoo ranks second in our security analysis based on the number of CVEs. Its vulnerabilities largely stem from the fact that the system offers a variety of integrated modules that create additional points where issues can emerge.
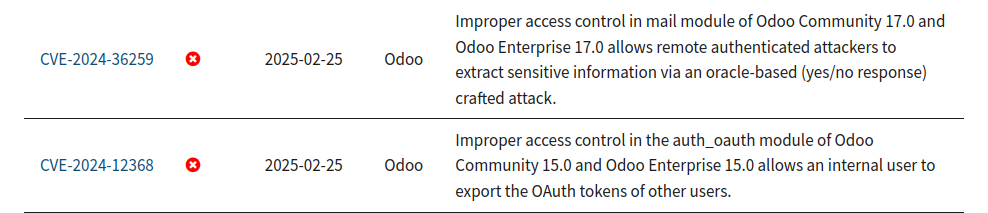
NVD data shows numerous CVEs for stored XSS, SQL injections, and sandboxing issues.

The peak years in this dataset were 2019 with 17 CVEs, 2020 with 13 CVEs, and 2023 with 14 CVEs, which became periods of heightened vulnerability exposure. Since then, reports appear less frequently
To Odoo’s credit, the company addresses security issues with regular security updates across both Community and Enterprise versions and systematic patching of reported vulnerabilities.
Vtiger
Issue Count: 71
Vtiger has been around for nearly two decades. As one of the oldest open-source CRMs, it has a substantial number of reported issues. Although many of them date back to the software’s early years, the solution continued to face regular security discoveries across nearly every year of development with only brief periods of visible stability.
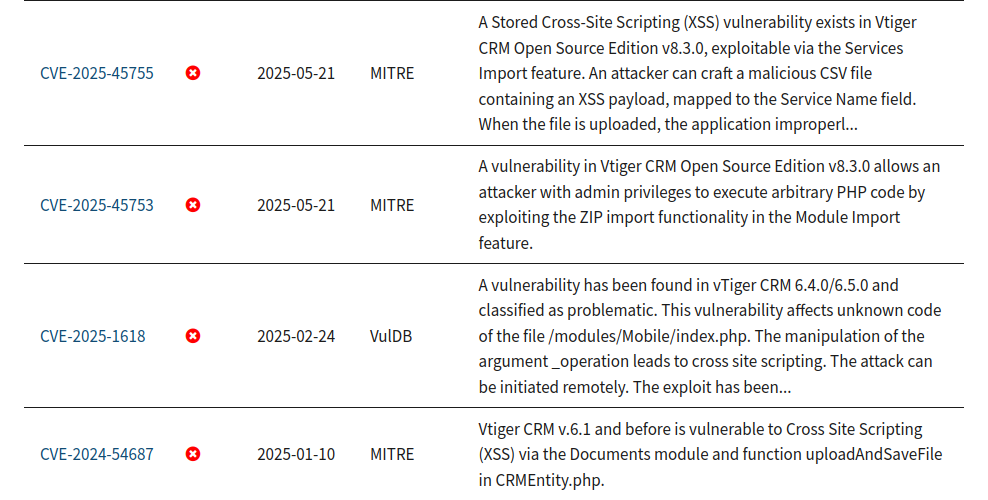
A review of 13 CVEs from 2023-2025 shows a concentration of XSS, SQL injections, and privilege escalation flaws. Several earlier versions allowed attackers to upload files with executable code. In some cases, it could lead to remote code execution on the server.

If you’re implementing the system for your needs, maintaining current patches and regular updates should be an ongoing and high-rank task taking into account the regular discovery of issues.
SuiteCRM
Issue Count: 85
SuiteCRM is one of the most widely used open-source CRMs that has a large and active community. The system has had a lengthy list of vulnerabilities, and about 66% of them were classified as high or critical severity.
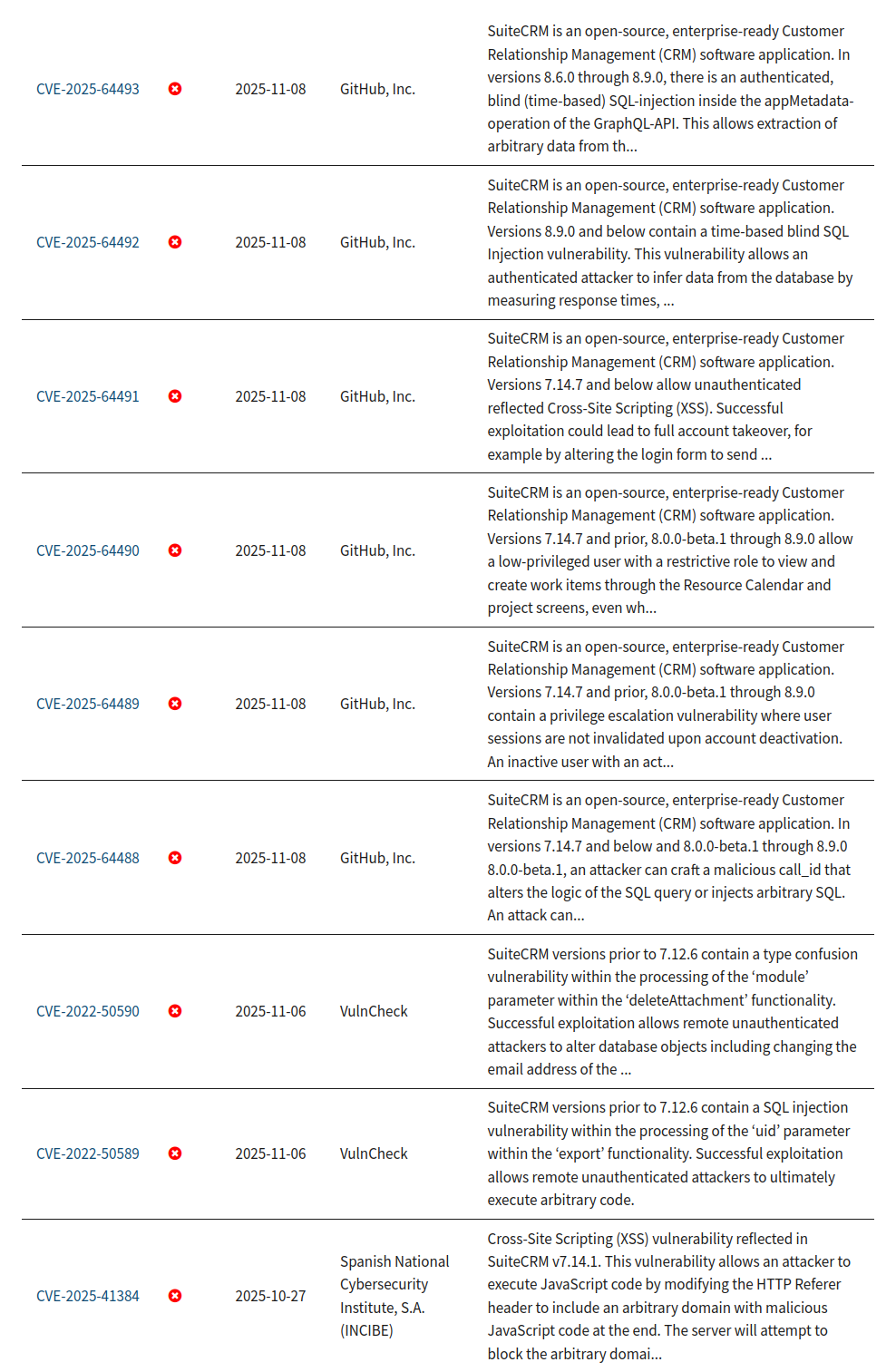
SQL injection vulnerabilities have been among the most prevalent and long-standing security risks in SuiteCRM. These flaws appear throughout the software modules: EmailUIAjax controllers, Tree data processing, Alerts system, and the SOAP API endpoints. Coupled with injection issues, both reflected and stored XSS have been common via email viewer, HTTP Referer headers, and Profile page fields.
Businesses using versions 7.14.6 and below face many significant risks, including even unauthenticated downloads of any file from the upload-directory and broken authentication mechanisms. Because these issues can expose sensitive data, it’s important to regularly update the software and implement strong security practices.
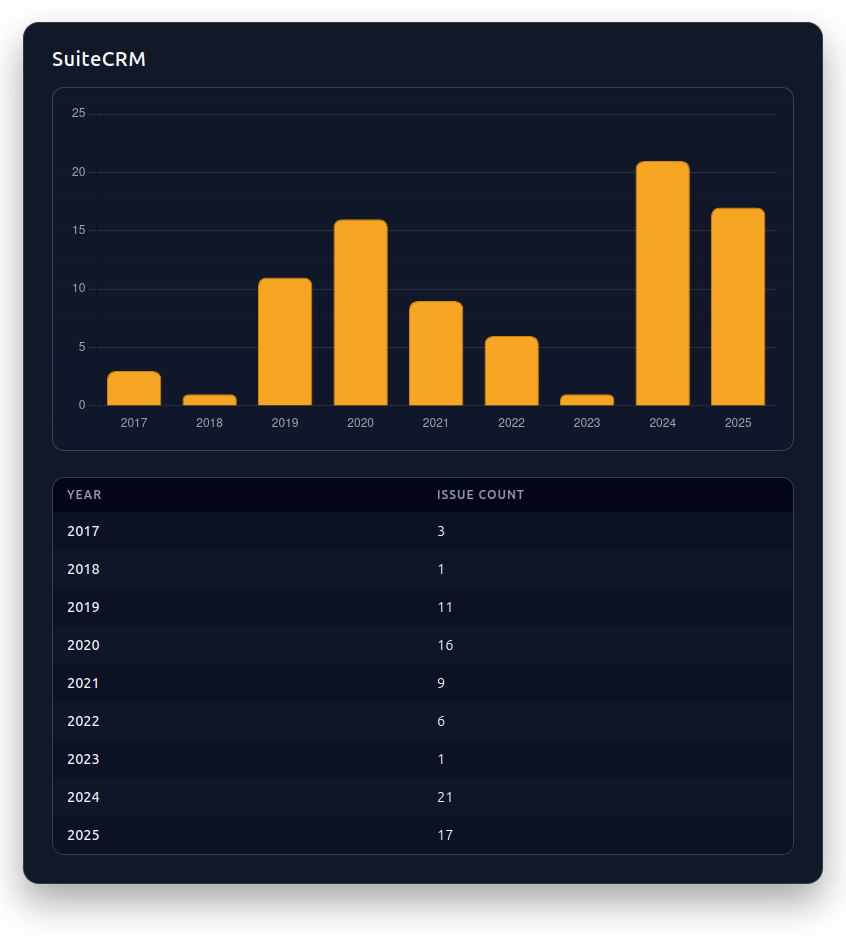
The NVD timeline reflects that the early adoption phase showed minimal documented issues (1-3 per year), but there was a significant surge in 2019-2020 with 27 issues recorded, including several serious SQL injection and remote code execution flaws. After a relatively quiet year 2023 (only 1 case), 2024 – 2025 witnessed a spike of 38 issues, which is the highest count on record.
Dolibarr CRM
Issue Count: 125
As the oldest platform reviewed, Dolibarr has one of the highest numbers of reported vulnerabilities among open-source CRMs. About half of these (63) were rated as high or critical severity.
Dolibarr has had XSS vulnerabilities (letting attackers inject malicious scripts into web pages), as well as more serious issues such as SQL injection vulnerabilities (which can expose or modify information stored in the database) and remote code execution (RCE), where attackers can run their own code on the server. In short, the software has lots of great modules and tools, but like any other solution, if it is left unpatched or misconfigured it can become a security risk.
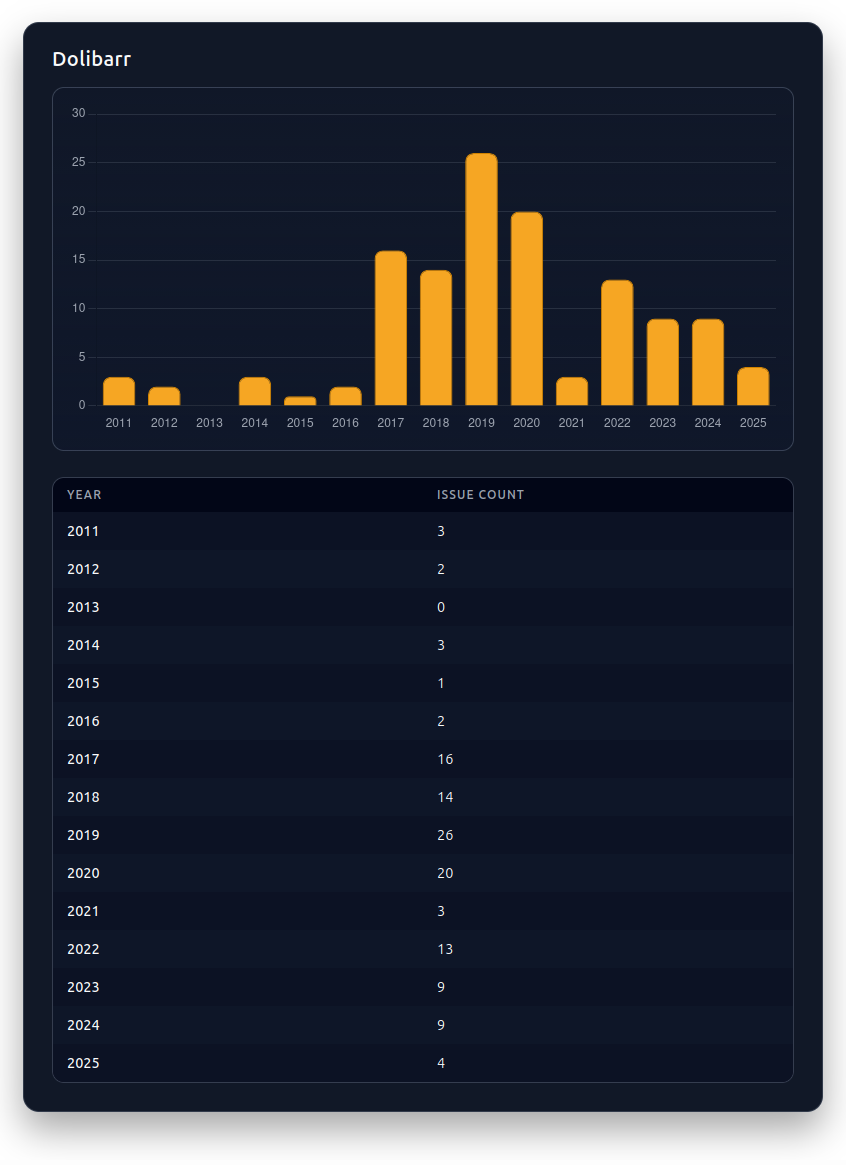
The platform experienced its most problematic period between 2017 and 2020, the CVE counts reached their peak at 26 issues in 2019. Recent versions show some security improvements, but the extensive vulnerability history suggests that legacy installations can face substantial risks.
Disclaimer: This analysis ranks selected open-source CRMs using publicly reported CVEs from the National Vulnerability Database as of November 12, 2025. Vulnerability counts and CVSS scores change over time and may be incomplete or version-specific. The presence of more CVEs does not necessarily mean a product is less secure. No warranty is given, use this information at your own risk. Consult vendor advisories and a qualified security professional before making decisions. Product names are trademarks of their respective owners.
